MAC Randomizer Alfred Script
A recent conversation I had dealt with free wifi that limited the amount of time you could use it before it kicked you off. Now, while I support the right of wifi providers to do as they please, it's an interesting question. AFAIK most tracking of that sort is done based on MAC addresses, which you can easily spoof if you want.
I wrote up a quick Alfred workflow that shells out from Python to do the real work. Note that if your wifi interface isn't called en0 this won't work for you.
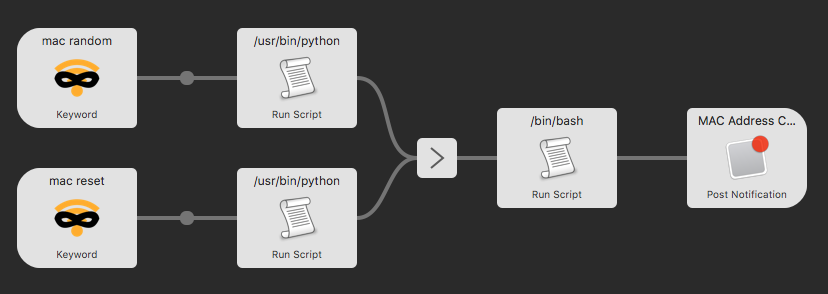
The first script shells out to ifconfig to get the current address. Which gives output like the following. We are interested in thatether f4:5c:89:b3:37:e1 line. The first three octets are of a MAC are the Organizationally Unique Identifier (OUI) and we don't need to change those, what we have is valid already.
en0: flags=8863 mtu 1500
ether f4:5c:89:b3:37:e1
inet6 fe80::8da:f24a:a0bb:3b7a%en0 prefixlen 64 secured scopeid 0x4
inet 192.168.1.126 netmask 0xffffff00 broadcast 192.168.1.255
nd6 options=201
media: autoselect
status: active Our script captures the OUI, then generates three more octets for the rest of the address, and prints it out.
from subprocess import check_output
from re import compile
from random import randint
MATCHER = compile("\W*ether ([a-f0-9]{2}:[a-f0-9]{2}:[a-f0-9]{2}:[a-f0-9]{2}:[a-f0-9]{2}:[a-f0-9]{2})")
output = check_output(["ifconfig", "en0"])
mac = None
for line in output.split("\n"):
match = MATCHER.match(line)
if match is not None:
mac = match.groups()[0]
break
prefix = mac[:8]
print "%s:%x:%x:%x" % (prefix, randint(0, 255), randint(0, 255), randint(0, 255))Next we need to actually set this new random MAC. This is a privileged operation, so if we passed it directly to ifconfig it would error out. Long story short, if we want a nice authorization dialog we have to pass through applescript, russian nesting doll style.
osascript -e "do shell script \"sudo ifconfig en0 ether {query} >/dev/null;\" with administrator privileges"I also added a way to reset it to the hardware value. The networksetup command handily has that for the taking. We just shell out, capture it and pass it through to ifconfig again.
from subprocess import check_output
from re import compile
MATCHER = compile("Ethernet Address: ([a-f0-9]{2}:[a-f0-9]{2}:[a-f0-9]{2}:[a-f0-9]{2}:[a-f0-9]{2}:[a-f0-9]{2})")
output = check_output(["networksetup", "-getmacaddress", "en0"])
match = MATCHER.match(output)
print match.groups()[0]You can download this workflow, comments and improvements appreciated.